As a self-proclaimed coffee enthusiast, I’ve always been intrigued by the complex journey our beloved brew takes from bean to cup. But recently, I’ve become increasingly aware of the pressing sustainability concerns that plague the coffee industry. It’s not just about the delicious flavor anymore – it’s about preserving the very ecosystems and communities that make coffee possible.
Unraveling the Tapestry of Sustainable Coffee
Sustainability in coffee production is a multifaceted concept that encompasses a commitment to practices ensuring the longevity of the coffee industry while minimizing negative impacts on the environment. It’s about supporting equitable economic structures and fostering social well-being – a harmonious blend of ecological, economic, and social considerations.
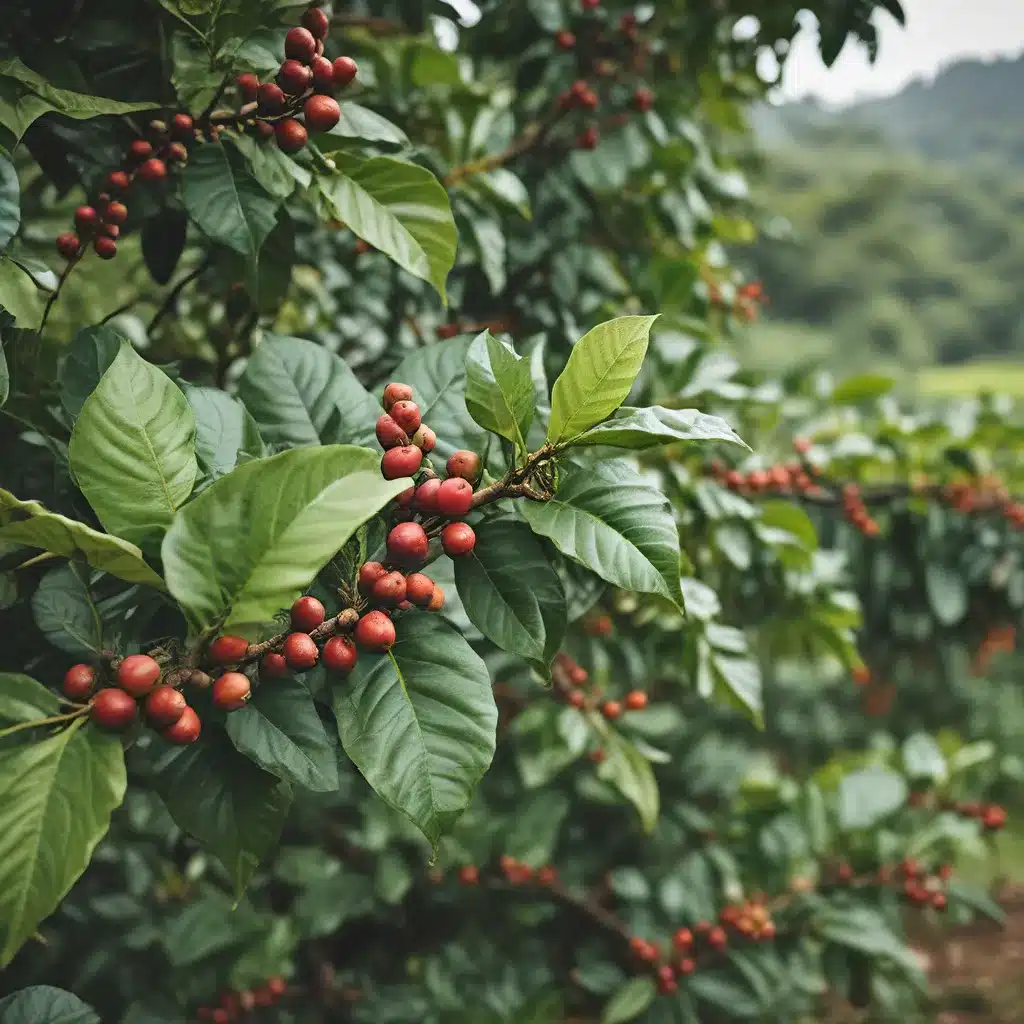
At the heart of sustainable coffee lies a deep respect for the natural world. Agroforestry, for instance, emerges as a leading approach, intertwining coffee plants with diverse trees to preserve biodiversity, prevent soil erosion, and foster a more resilient ecosystem. The synergy between coffee and the natural environment ensures a balance that minimizes the need for chemical interventions, thus preserving the delicate ecological equilibrium.
But sustainability doesn’t stop at environmental conservation – it extends to the very livelihoods of coffee growers and processors. Fair trade practices, a cornerstone of sustainability, ensure that these essential contributors receive fair compensation for their efforts. Beyond economic stability, sustainability initiatives often include community development projects such as education and healthcare, enhancing the overall well-being and empowerment of those involved in the coffee supply chain.
The Perils of Unsustainable Coffee Production
The significance of sustainability in the coffee industry cannot be overstated, considering its pervasive impact on the environment, communities, and the overall quality of the coffee produced. Unsustainable farming practices contribute to deforestation, habitat destruction, and soil degradation. Moreover, conventional processing methods and excessive water usage can lead to pollution and strain on local water resources.
The economic and social implications of unsustainable coffee production are far-reaching. Unfair compensation, exploitative labor practices, and neglect of social development lead to weakened communities. Sustainable coffee practices, on the other hand, promote fair wages, community empowerment, and improved living conditions, fostering resilience and stability.
Addressing Sustainability Challenges in Coffee
Sustainability concerns in the coffee industry demand urgent attention to secure a future for coffee production and the well-being of the communities involved. Let’s dive deeper into some of the critical issues and the innovative solutions emerging to address them.
Deforestation: A Pressing Concern
Deforestation remains a pressing concern in the coffee industry, as the expansion of coffee plantations often involves clearing large areas of forests, leading to habitat loss, diminished biodiversity, and disrupted ecosystems. Sustainable farming practices, including agroforestry and reforestation programs, address this concern by promoting coexistence with existing ecosystems.
Water Usage: Conserving a Precious Resource
Water usage poses a significant threat to sustainability in coffee production. Traditional irrigation methods and excessive water consumption in processing contribute to water scarcity and environmental degradation. Sustainable approaches emphasize water-efficient irrigation systems, rainwater harvesting, and the adoption of agroecological practices to ensure responsible water use.
Climate Change: Adapting for the Future
Climate change emerges as a formidable threat to coffee species, impacting the suitable growing areas and overall production. Rising temperatures, erratic rainfall patterns, and increased prevalence of pests and diseases jeopardize coffee cultivation. Sustainable initiatives involve research into climate-resilient coffee varieties, adaptive farming practices, and comprehensive strategies to safeguard the diversity and longevity of coffee species.
Certifications and Standards: Signposts for Sustainability
Determining the sustainability of coffee involves understanding the certifications, practices, and criteria that signify a commitment to ecological, economic, and social well-being. Certification labels serve as trustworthy indicators of a coffee’s sustainability, with recognized labels such as Rainforest Alliance, Fair Trade, and USDA Organic signifying adherence to stringent standards.
These standards often encompass environmentally friendly farming practices, fair labor conditions, and support for community well-being. Third-party certifications in the coffee industry entail rigorous criteria, empowering consumers to make informed choices aligned with their sustainability values.
Sustainable Practices in Coffee Cultivation
Sustainable coffee production involves a set of practices that prioritize environmental stewardship and ethical considerations throughout the cultivation and processing stages. Implementing sustainable practices in coffee cultivation requires a focus on better crop management.
Organic farming methods, which eliminate synthetic pesticides and fertilizers, create a healthier ecosystem. Integrated pest management minimizes environmental impact, while precision agriculture optimizes resource use for sustainable cultivation. By embracing these sustainable practices, the coffee industry actively seeks to reduce its environmental footprint.
Promoting Economic Sustainability for Coffee Farmers
Promoting economic sustainability for coffee farmers involves adopting practices that ensure fair compensation and eliminate exploitation. Fair compensation is integral to economic sustainability, as sustainable initiatives, including fair trade practices, ensure that farmers receive a fair price for their coffee. This fair compensation empowers farmers to invest in their farms, communities, and future endeavors, creating a foundation for long-term economic stability.
Avoiding the exploitation of coffee farmers necessitates the implementation of ethical practices and transparent supply chains. Sustainable initiatives actively work against exploitative practices by ensuring fair wages, safe working conditions, and transparent trade relationships, fostering a supportive and equitable environment for farmers.
Addressing Social Sustainability Challenges
While sustainability initiatives aim to enhance the social aspects of coffee farming, challenges persist that impact the well-being of farmers and their communities. Low wages remain a significant challenge to social sustainability, as unsustainable practices and unfair compensation structures contribute to economic disparities and social inequalities. Sustainable initiatives, including fair trade practices and advocacy for living wages, seek to address this challenge and uplift the social fabric of coffee-producing communities.
Labor exploitation poses another serious threat to the social sustainability of coffee farming. Unethical practices, including child labor, discrimination, and unsafe working conditions, undermine the well-being and dignity of workers. Sustainable coffee production actively opposes labor exploitation, promoting fair and ethical treatment to create socially responsible farming environments.
The overall impact of sustainable coffee production on local communities is profound. Beyond economic contributions, such as fair compensation and community development projects, social sustainability initiatives enhance education, healthcare, and gender equality, resulting in empowered and resilient local communities with improved living standards.
Sustainability Initiatives and Certifications
Numerous initiatives and programs are in place to elevate sustainability in coffee-producing regions, addressing environmental conservation, social development, and economic stability. Let’s explore some of the key players in this transformative movement.
Rainforest Alliance Certification
The Rainforest Alliance Certification plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability by focusing on environmental conservation, social equity, and economic viability. The certification encourages agroforestry, biodiversity conservation, and fair labor practices, making a positive impact on coffee-producing regions.
Shade-Grown Coffee
Shade-grown coffee practices contribute significantly to sustainability by promoting biodiversity and environmental conservation. These practices involve cultivating coffee under the canopy of trees, reducing the need for pesticides and creating a symbiotic relationship between coffee plants and the natural ecosystem.
Organic Certification
Organic certification in coffee production ensures that farming practices are free from synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. This commitment to organic methods promotes soil health, biodiversity, and environmental sustainability, providing consumers with confidence in choosing environmentally friendly coffee options.
Fair Trade Certification
Fair Trade and sustainable coffee share a strong connection, as both movements strive to create a fair and equitable coffee industry that prioritizes the well-being of farmers and the environment. Fair Trade Certification signifies a commitment to ethical and sustainable practices, ensuring safe working conditions, fair wages, and equitable treatment of workers. By choosing Fair Trade Certified coffee, consumers actively support a supply chain that prioritizes both social and environmental sustainability.
Innovations Driving Sustainability Forward
Innovations and technologies play a crucial role in advancing sustainability in coffee farming, addressing environmental impact, improving efficiency, and ensuring the resilience of coffee production. The Sustainable Coffee Challenge serves as a catalyst for innovation, encouraging the development and adoption of sustainable practices through collaborative efforts across the industry.
Technological advancements, such as precision agriculture and sustainable processing methods, contribute to enhancing sustainability in coffee farming. Innovations in crop breeding for climate resilience and disease resistance also ensure the long-term sustainability of coffee cultivation.
Overcoming the Challenges of Transitioning to Sustainable Practices
Transitioning to sustainable coffee practices is not without challenges, as farmers and stakeholders encounter initial hurdles that require investment, education, and commitment. Investments in organic certification, training programs, and transitioning from conventional to sustainable methods can be financially demanding. However, the long-term benefits, including improved soil health and market access, often outweigh the initial challenges.
Education and awareness are critical in overcoming challenges related to sustainable coffee production. Farmers need access to information about sustainable practices, certification requirements, and the potential benefits. Consumer awareness also plays a role in creating demand for sustainable coffee, incentivizing farmers to adopt environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices.
Protecting Forests and Restoring Ecosystems
Deforestation is a significant concern in coffee-producing areas, and concerted efforts are underway to mitigate its impact and promote sustainable land use. Sustainable farming practices, such as agroforestry, actively contribute to combating deforestation by preserving natural habitats and enhancing biodiversity.
Reforestation programs play a vital role in addressing deforestation in coffee-producing areas. These programs involve planting native trees, restoring degraded land, and creating buffer zones around coffee plantations. Reforestation contributes to carbon sequestration, protects water sources, and restores ecological balance in coffee regions.
Conservation initiatives are also instrumental in protecting natural habitats in coffee regions. These efforts focus on preserving biodiversity, supporting wildlife corridors, and creating sustainable landscapes. By partnering with local communities and organizations, conservation initiatives aim to ensure the long-term health of ecosystems affected by coffee production.
The Rise of Sustainable Coffee Brands
Sustainability in coffee extends beyond farming practices to include the entire supply chain, and a sustainable coffee brand is characterized by its commitments, transparency, and ethical practices.
Transparent sourcing is a cornerstone of a sustainable coffee brand. Brands that openly communicate their sourcing practices, including the origin of beans, farming methods, and adherence to certifications, build trust with consumers. Transparent sourcing ensures accountability and allows consumers to make informed choices that align with their sustainability values.
Sustainable coffee brands are defined by their commitments and ethical practices. This includes fair trade certifications, environmentally friendly farming methods, support for social initiatives, and efforts to minimize the overall ecological footprint. These commitments reflect a brand’s dedication to holistic sustainability across the entire supply chain.
Ethical coffee production centers on fair compensation for coffee growers, safe working conditions, and adherence to principles that prioritize the well-being of workers and communities. Ethical brands openly share information about the origin of their beans, the conditions of coffee farmers, and the overall supply chain, allowing consumers to verify ethical practices and support brands committed to fair and sustainable sourcing.
The Price of Sustainability: Balancing Fairness for Farmers
The price of coffee and its sustainability are interconnected, with fair compensation for farmers playing a pivotal role in fostering a sustainable coffee industry. Balancing fair prices for farmers is integral to coffee sustainability, as fair compensation ensures that farmers can invest in sustainable farming practices, improve their living standards, and contribute to environmental conservation.
A fair pricing model supports the economic viability of coffee farming, fostering long-term sustainability. Consumer awareness and support are essential for the sustainability of coffee prices, as informed consumers who actively seek and support sustainably produced coffee create a demand that encourages fair pricing models. The collective voice of conscious consumers plays a crucial role in shaping the economic sustainability of the coffee industry.
Transparency and Traceability: Keys to Sustainable Coffee
Coffee companies committed to sustainability actively implement measures to ensure transparency in their sourcing and overall sustainability practices. These companies provide openness about farming location and practices through clear communication channels, including detailed information on packaging, websites, and marketing materials. Openness fosters trust with consumers and demonstrates a commitment to transparency.
Traceability of beans from farm to cup is a priority for coffee companies embracing sustainability. These companies implement traceability measures such as batch tracking, certifications, and partnerships with transparent supply chain partners. By tracing the journey of coffee beans, companies can verify sustainable and ethical practices at every stage of production.
The Power of Consumer Choice: Driving Sustainability
Consumers wield significant influence in promoting coffee sustainability through their choices, preferences, and demand for ethical and environmentally friendly practices. Consumer choice directly impacts the promotion of sustainability in coffee, as consciously choosing certified sustainable and ethical coffee signals a demand for responsible practices.
This demand, in turn, encourages coffee companies to adopt and adhere to sustainable and ethical standards, creating a positive cycle of consumer-driven sustainability. Consumers supporting brands with ethical practices in the coffee industry contribute to the overall improvement of sustainability standards, driving positive change in the industry.
Choosing Sustainable Coffee: A Guide for Enthusiasts
Coffee enthusiasts can actively contribute to sustainability by making informed choices and supporting practices that prioritize environmental and social well-being. Choosing certified sustainable coffee involves selecting beans with recognized certifications such as Rainforest Alliance, Fair Trade, or USDA Organic. These certifications signify adherence to strict sustainability standards and offer consumers confidence in the ethical and environmental credentials of their chosen coffee.
Supporting brands with transparent and ethical practices is a powerful way for coffee enthusiasts to promote sustainability. By favoring brands that openly communicate their sourcing, sustainability initiatives, and ethical commitments, consumers create a demand for transparency and ethical conduct in the coffee industry.
Navigating the Spectrum of Sustainable Coffee Options
Different types of coffee align with varying degrees of sustainability, with certain characteristics and certifications indicating a commitment to environmentally friendly and socially responsible practices.
Shade-grown coffee contributes significantly to sustainability by preserving biodiversity and minimizing the environmental impact of coffee cultivation. This method involves growing coffee under the canopy of diverse trees, creating a natural habitat that supports wildlife and reduces the need for synthetic inputs.
Rainforest Alliance Certified coffee is a sustainable choice due to its adherence to rigorous environmental, social, and economic standards. The certification ensures responsible land use, conservation of biodiversity, fair treatment of workers, and support for community development initiatives.
Organic coffee aligns with sustainability principles by eschewing synthetic pesticides and fertilizers. Organic farming methods prioritize soil health, biodiversity, and environmental conservation, making organic coffee a sustainable choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Navigating the Environmental Challenges of Coffee Production
As I delve deeper into the sustainability landscape of coffee, I can’t help but be struck by the significant environmental challenges that plague the industry. Water usage, for instance, is a critical factor contributing to the environmental impact of coffee production. Conventional irrigation methods and water-intensive processing practices can lead to depletion of local water resources and pollution.
Sustainable coffee production, however, focuses on efficient irrigation, rainwater harvesting, and water-conscious processing to mitigate these environmental impacts. By adopting these practices, the coffee industry can strike a better balance between its thirst for water and the needs of the local communities and ecosystems.
Another pressing concern is deforestation, which significantly contributes to the carbon footprint of coffee production. Clearing land for expanding coffee plantations releases stored carbon, disrupts ecosystems, and exacerbates climate change. Sustainable farming practices, including agroforestry and reforestation, actively address this concern by integrating trees into coffee plantations and preserving natural habitats.
Confronting the Challenges of Climate Change
Climate change poses a multifaceted challenge to coffee sustainability, impacting growing conditions, yields, and overall production. As the climate continues to shift, the suitable growing areas for coffee are being pushed to higher altitudes and latitudes, while rising temperatures and unpredictable weather patterns affect the quality and flavor profile of coffee.
Sustainable initiatives involve research into climate-resilient coffee varieties and adaptive farming practices to ensure the continued viability of coffee cultivation. These efforts address the diverse effects of climate change, such as altered rainfall patterns, increased incidence of pests and diseases, and extreme weather events that threaten the stability and yields of coffee crops.
By embracing sustainable approaches and fostering resilient coffee production, we can safeguard the future of this beloved beverage and the communities that depend on it. It’s a complex challenge, but one that I’m committed to tackling, one cup of sustainable coffee at a time.
Conclusion: Cultivating a Sustainable Coffee Future
Sustainability in coffee encompasses a holistic approach that considers environmental, economic, and social factors. From agroforestry and fair trade practices to technological innovations and consumer choices, each aspect plays a crucial role in shaping a sustainable coffee industry.
By understanding the multifaceted nature of coffee sustainability and actively supporting ethical and environmentally friendly practices, stakeholders can contribute to a resilient and thriving future for the global coffee community. As I sip my sustainably sourced cup of coffee, I’m reminded of the power we all hold in shaping the future of this beloved beverage.
So, let’s raise our mugs to a more sustainable, equitable, and environmentally